Digital Audiovisual Properties - Advanced
Peter Bubestinger-Steindl
(peter @ ArkThis.com)
October 2022
Aspect Ratio
“Is the size relationship between width (x) and height (y) of an image.”
Usually written as a fraction: width:height (eg
16:9)
Aspect Ratio
Most people only mean/know the “Display Aspect Ratio” (DAR).
- 4:3 (1,33333…)
- 16:9 (1,777777…)
- 5:4 (1,25)
1920 / 1080 =
1,7777777777778
DAR… SAR? PAR!
- DAR: Display Aspect Ratio
What it should be shown/seen like. - SAR: Storage Aspect Ratio
What the stored image pixel width/height ratio is. - PAR: Pixel Aspect Ratio
What the physical dots on your screen have.
Formula: DAR = SAR x PAR
Anamorphic Video
| Format | DAR | SAR | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digibeta | 16:9 | 5:4 | 720 x 576 |
| HDV | 16:9 | 4:3 | 1440 x 1080 |
Anamorphic Video
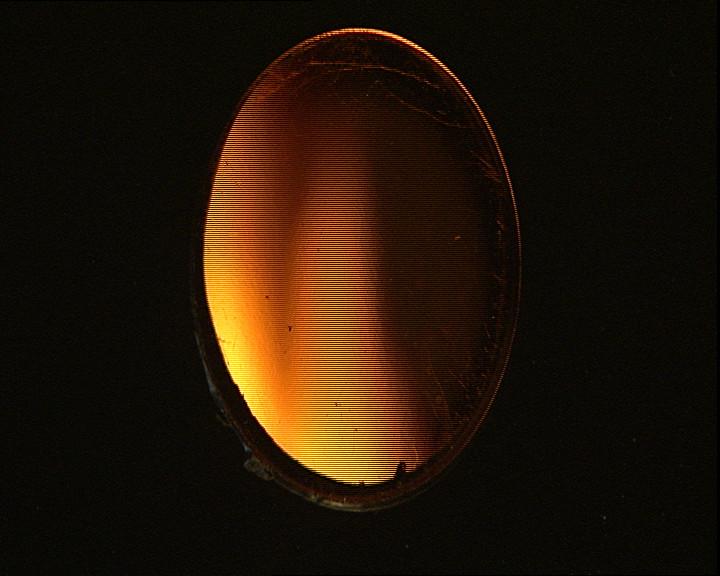
 Left:
Actual Source — Right: DAR applied
Left:
Actual Source — Right: DAR applied
Good to know
DVD SAR = 5:4
So 16:9 is either letterboxed or anamorphic.
HD is always DAR=16:9
4:3 in HD is impossible without editing.
Links
Interlacing
Ever wondered what 720i, 576i or 1080p means?
- p = progressive (full-frame)
- i = interlaced
Interlacing
- Opposite is “progressive” (=full image frame)
- 2 fields in one frame: 1 Top, 1 Bottom
- Field: half of vertical resolution
- Field: twice the time resolution
(25i fps = 50 images)



Top Field

Bottom Field

Field order
- TFF: Top Field First
- BFF: Bottom Field First
- Progressive: Full-frame, no interlacing.
The correct field order is relevant for correct display of motion.
Store this metadata!
Links
GOP: Group Of Pictures
The GOP is a group of pictures in a video that are depending on each other.
GOP Frametypes
- [I]ntra:
Independently encoded single frame (aka “keyframe”) - [P]redictive-coded:
Difference-informations to previous I- or P-Frame. - [B]idirectional predictive-coded:
Difference-informations to previous and/or subsequent I- or P-Frame.
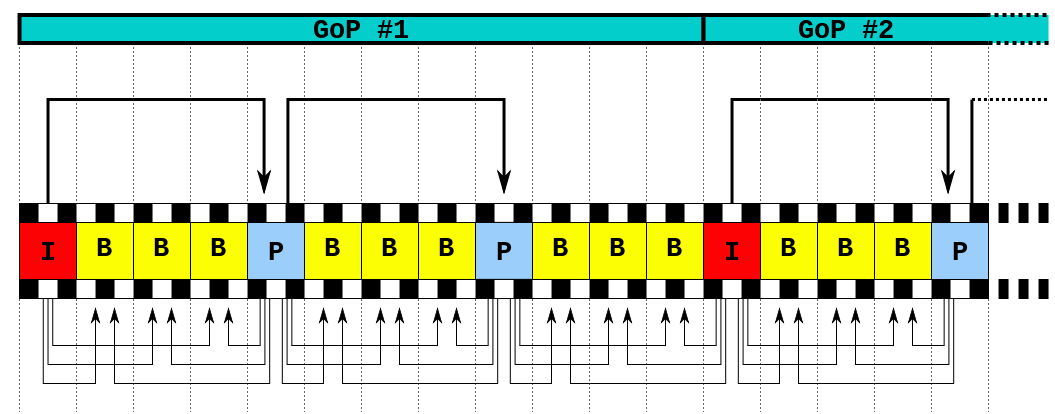
GOP and Recording
- Recording should be done with GOP=1.
- This means:
only I-Frames (=no dependencies between frames).
GOP and Editing
- With GOP = 1: No issues.
- With GOP > 1: Watch out!
btw: Some (but not all) video editing programs are able to perform “GOP-aware” cuts
Links
Color models
Note: Those are just 2 for video. There are more…
Color Model: RGB
Color Model: YUV


Shades of Gray
(=Bits Per Component/Sample)

Color Components
- RGB:
Red, Green, Blue - YUV:
Y’, Cb, Cr
Bits Per Component/Sample
| BPC | Gray shades | Pixel | Byte(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 2^8 = [0..255] | 24 Bits | 3 Bytes |
| 10 | 2^10 = [0..1023] | 30 Bits | 6|4 Bytes |
| 16 | 2^16 = [0..65535] | 48 Bits | 6 Bytes |
Chroma Subsampling
The color information in YUV is stored in a reduced resolution. (compared to its B/W component)
This principle originates from analog transmission and was kept in digital, because it allows smaller data sizes.
“J:a:b” Notation
| J: | Horiz. sampling reference (usually “4”). |
| a: | Number of color samples in 1st row of J pixels. |
| b: | Number of change in color samples between 1st / 2nd row of J pixels. |
Chroma Subsampling
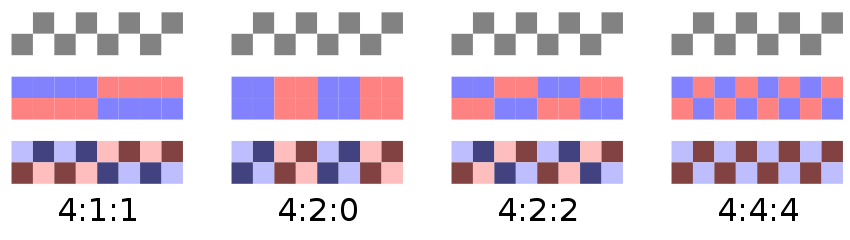
Preserve subsampling as-is, if possible.
Diskspace
1s Image = Width*Height * FPS * 3*BPC / 8 (=Bytes)
| BPC | Size (4:2:2) | Size (4:4:4) |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 1.16 GB | 1.74 GB |
| 10 | 1.45 GB | 2.17 GB |
| 16 | 2.32 GB | 3.48 GB |
Example shows: 1 minute uncompressed PAL SD
