Introduction to Data and Encoding
Peter Bubestinger-Steindl
(peter @ ArkThis.com)
November 2022
What do you think
happens when you open a file?
How do you think
a program/machine identifies a file?
How do YOU usually
identify a file?
What is there to identify?
What is a digital file?
![]()
What kind of files exist?
- documents?
- images?
- executables?
- …?
- anything else?
Understanding digital objects
- Bit:
A single binary digit (0/1) - Byte:
A unit: 8 bits (half = Nibble) - File:
Stored segment or block of information available to a computer program - File
system:
A mechanism for controlling and organizing bytes into structure (files/folders) for storage and retrieval - File
Format:
A standard way that information is encoded in a computer file.
Identifying files
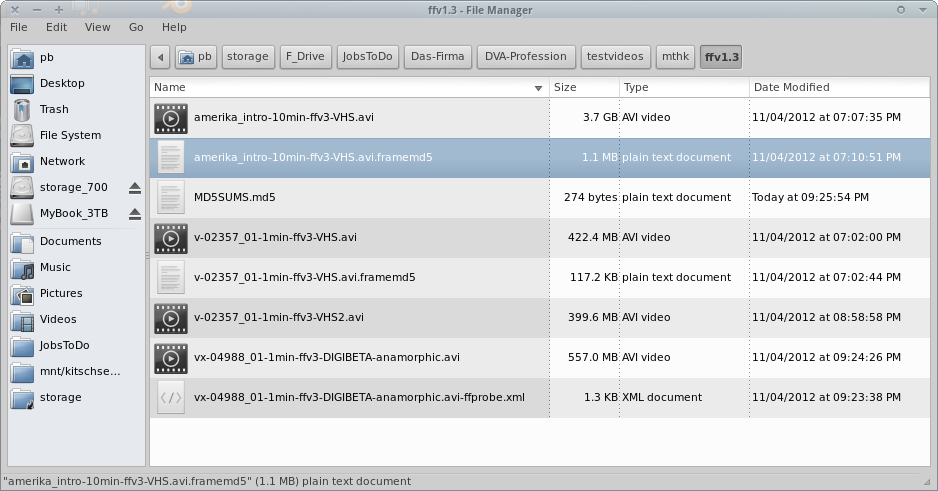
The Filesystem
- Filename
- Date/time
- Filesize
- File extension
- Path
- Access rights
What is Data?
The 2 major types of Data
Text:
Literally “just” text characters.Binary:
Data for machines/programs.
Not intended to be viewed directly by humans.
btw: Most “text documents” (docx, odt, pdf) are not text. They are binary data.
Everything’s a number
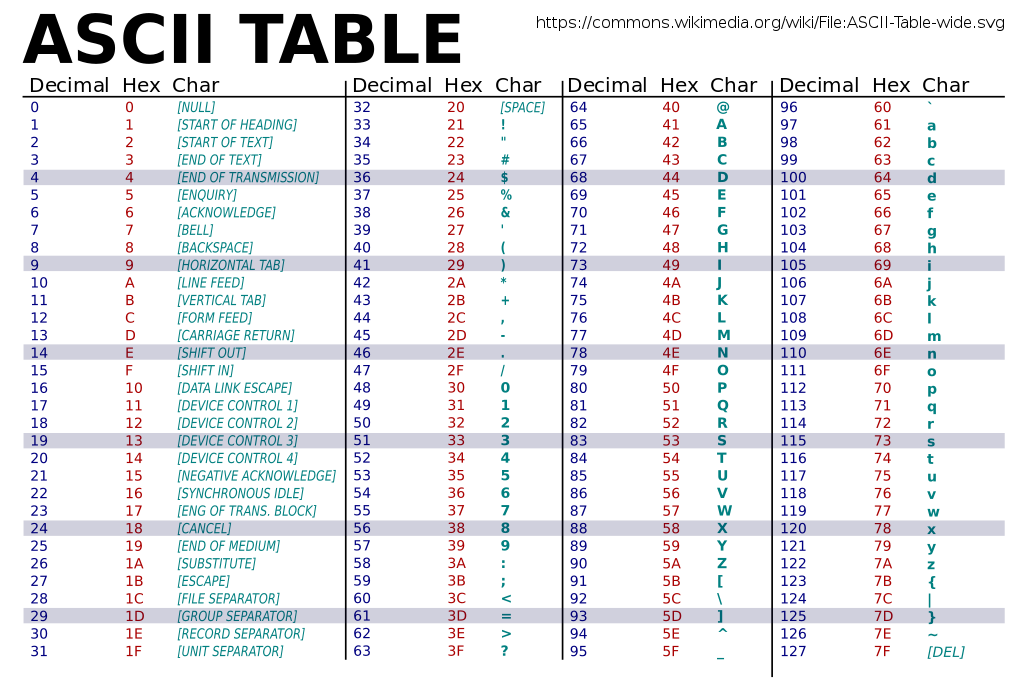
Character encoding tables
See: Character sets, encodings, and Unicode (By Nick Gammon)
Unicode
“Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world’s writing systems.” – Wikipedia: Unicode
Mixing languages
Лорем ипсум долор сит амет
側経意責家方家閉討店暖育田庁載社
पढाए हिंदी रहारुप अनुवाद कार्यलय
국민경제의 발전을 위한 중요정책의
旅ロ京青利セムレ弱改フヨス
غينيا واستمر العصبة ضرب قد. وباءت
See: UTF-8 encoding table
Unicode Symbols
- U+1F973 🥳
- U+262F ☯
- U+1F643 🙃
- U+1F9A0 🦠
See: Emoji List, Emojipedia
Comments?
Questions?