Topic 5 - Archival Storage
Reality check
- “Just storing files” is not preservation
- Storage market focus may deviate from your use case
- There’s more than just one right solution…
- Mixing is usually a good idea.
Physical Media Types
Optical Disks

HDD: Hard Disk Drive

Data Tape

Flash Memory
Media Types: Overview





HDD vs SSD
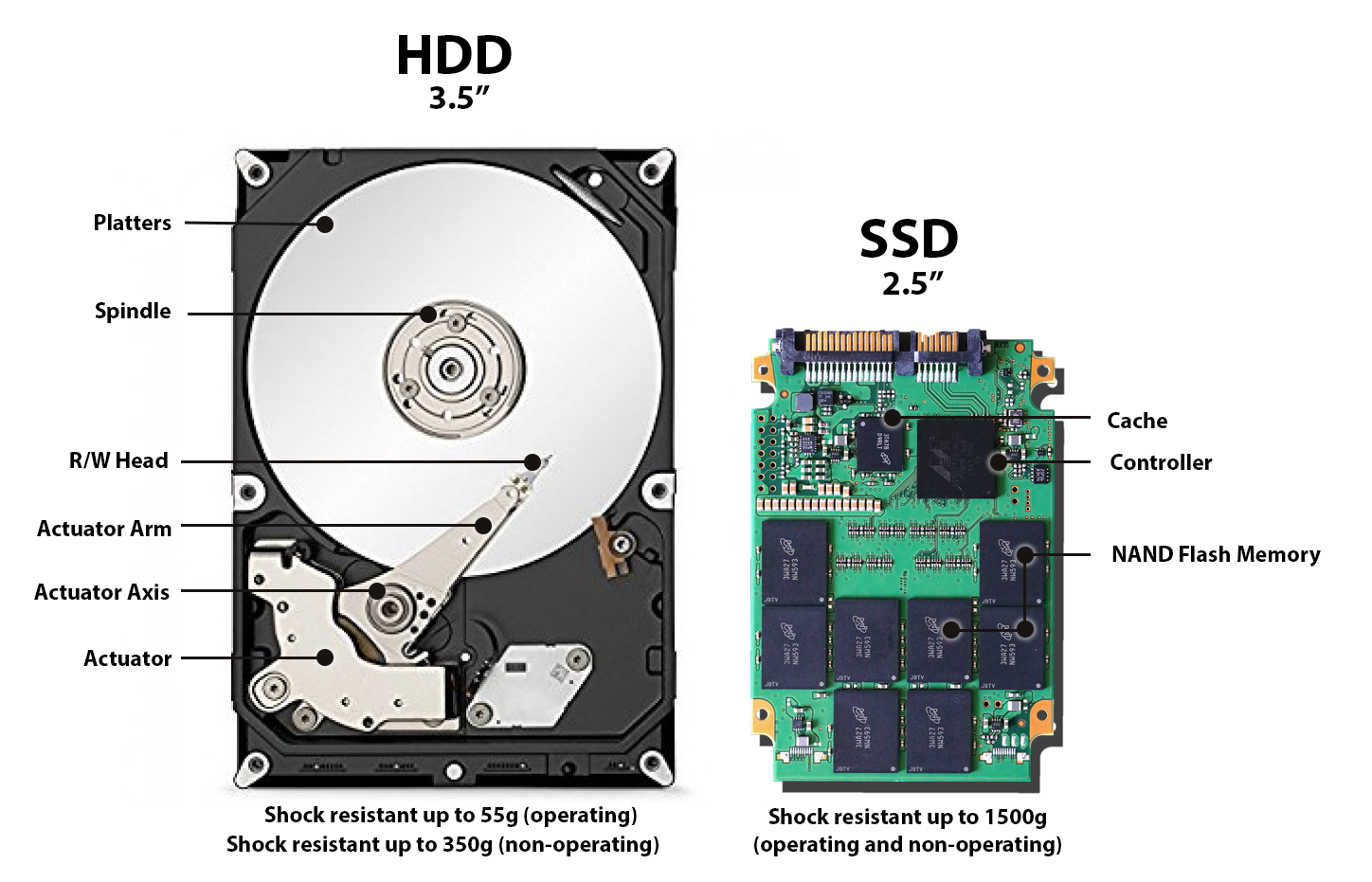
Good to know:
- Higher data density = more impact of an error.
Example: 1mm hole in CD vs DVD vs BluRay - or SD vs MicroSD, etc. - HDD: The longer it is active, the shorter is lives.
- But: “Hardware that lies, dies.”
- Be aware if your HDD is “Shingled (SMR)” or not.
Storage Types
External Hard Disks
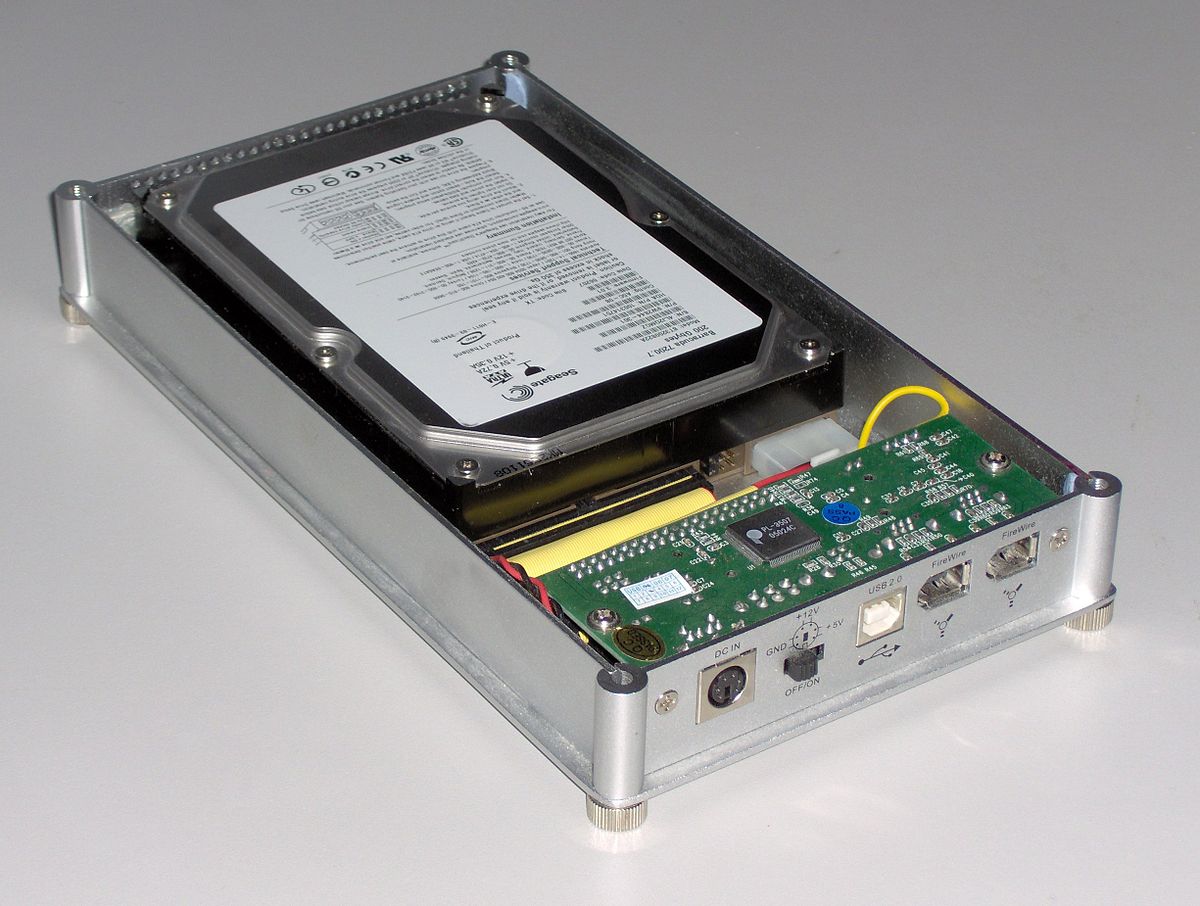

External Hard Disks
Ideal for:
* Collections ≤ [size of largest HDD] * Accessed by only 1 computer at a time * Moving data * Quick access
Advantages:
* Relatively low cost (100-300 EUR) * Portable
Disadvantages
* Risky: Drives may fail * Backup is manual and easily out of sync * Access is limited
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
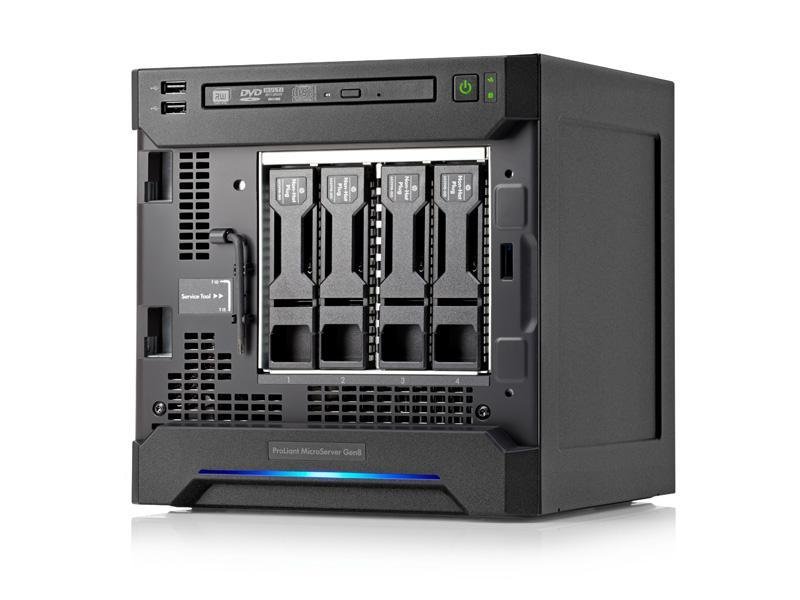

Network Attached Storage (NAS)
Ideal for:
* Collection < ca. 40 TB (if standalone). * Larger is possible, if clustered. * Quick access (incl. multiple networked users) * Networks with ≤ 1 GbE for large files (10 GbE for film) * Organizations with some IT support
Advantages:
* Multiple users can access in parallel * Relatively affordable (200-1000+ EUR)
Disadvantages:
* Requires heating / cooling * Potentially less secure (always on) * Less portable * Requires IT skills for problem solving
Data Tape
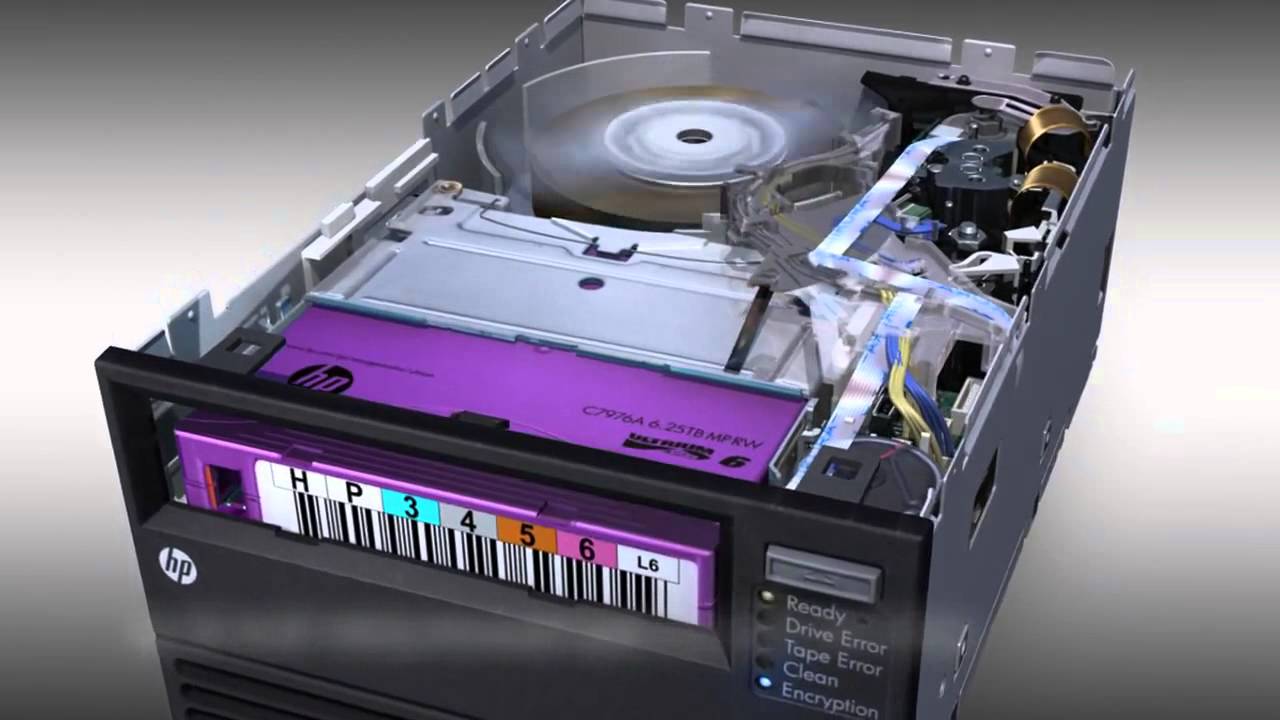

Data Tape
Ideal for:
* Collections from 10 TB to x PB * Collections that don’t need to be accessed in seconds * Back up scenarios
Advantages:
* Relatively low cost for tape stock * Scalable * Portable * Low failure rates
Disadvantages:
* Offline or nearline * Management & migration can be challenging * Proprietary tape filesystems
Data Tape Library (Robot)

LTO Generations
Imagine you find an old LTO tape…
- Not every drive can read every tape.
- New LTO generation release: ~every 2-3 years.
- < LTO-7: Read=2 gen. / Write=1 gen.
- BUT: LTO-8: Read/write=1 gen.!
The Cloud

The Cloud
Ideal for:
* Collections from any size * Institutions with limited IT support * Collections that don’t need to be accessed immediately * Fast access to smaller resolution files (streaming)
Advantages:
* Only pay for what you use * Scalable * Reduces the day-to-day management needs * AV: Low-resolution access scenarios
Disadvantages:
* HTTP access can be very slow for large files * Requires careful planning to ensure the correct services are being purchased * Depends on Internet connection * Vendor migration/lock-in
Storage Debate!
Networks
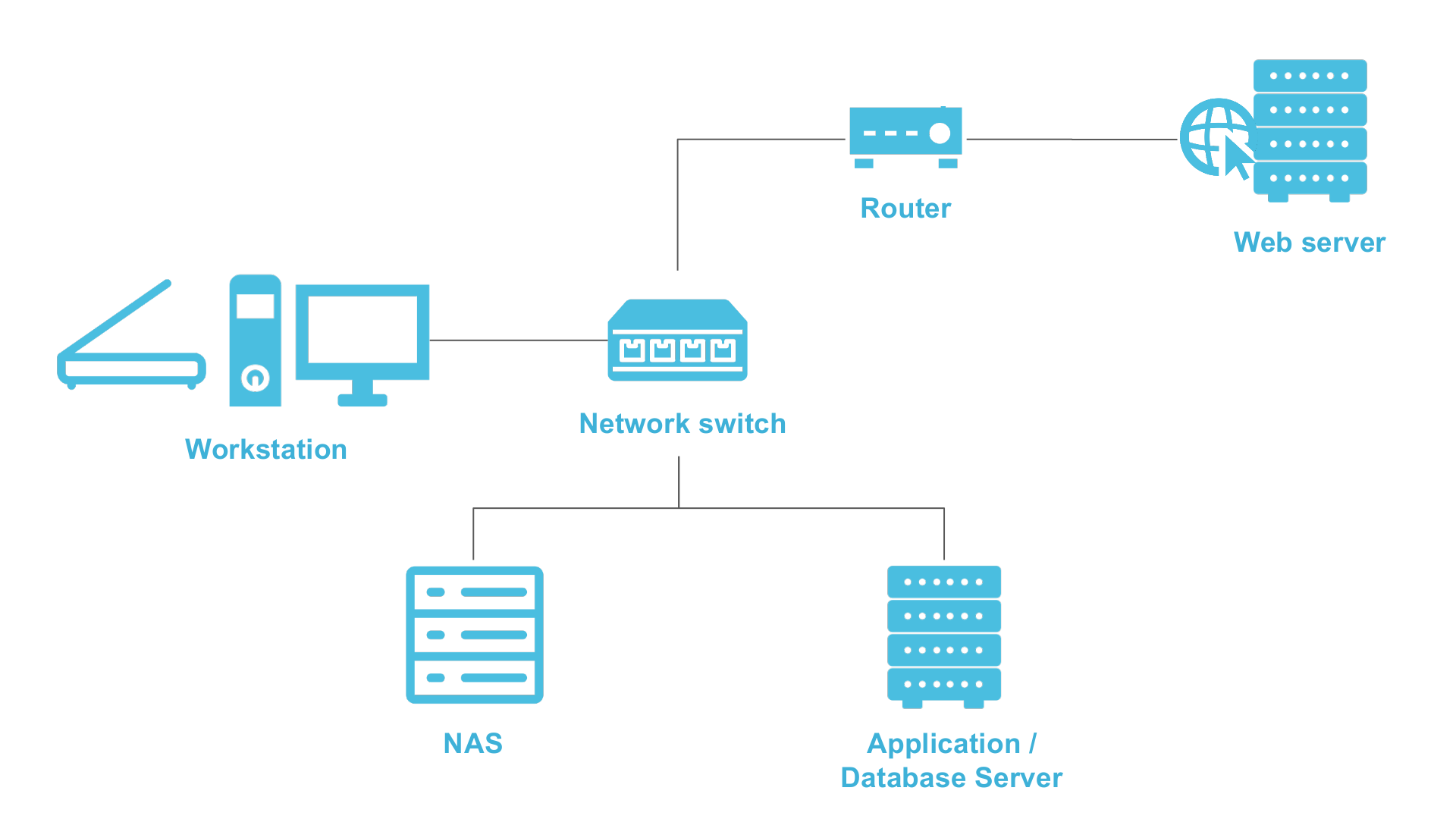
Consider: Layers!

The File System
The File System?
- Raw storage = unstructured chain of bits
- File system (FS) = file/folder structure
- Different FS = different formats:
- FAT{16,32} (Microsoft)
- NTFS (Microsoft)
- EXT{2,3,4} (Linux *)
- ZFS (Sun *)
- HFS+ (Apple)
- LTFS (IBM *)
(*) Open formats
LTFS: Linear Tape File System
- Open specification = vendor neutral
- Better for preservation, but may not support “convenience” features.
- All implementations must:
- Correctly read media that was compliant with any prior version.
- Write media that is compliant with the version they claim compliance with.
File system: Disaster relevant?
- Deleted files are still there (maybe fragmented).
- Different FS = different error resilience and recovery options.
- Does it scale? (moving files is when they’re most vulnerable…)
- Tools/knowhow to deal with recovery of broken filesystems in your setups?
- Logical Volume Management (LVM) snapshots
Errors? Backup!


The 3-2-1 Backup Rule
- Keep at least three copies of your data.
- Store two backup copies on different devices or storage media.
- Keep at least one backup copy offsite.
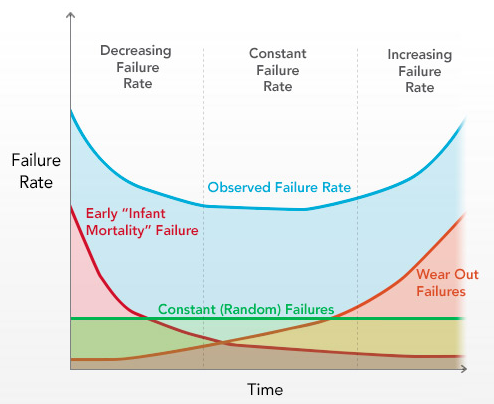
Statistics of HDD failure
The Story of ToyStory2

Data errors

Digibeta Dropouts

Audio Bit-Errors
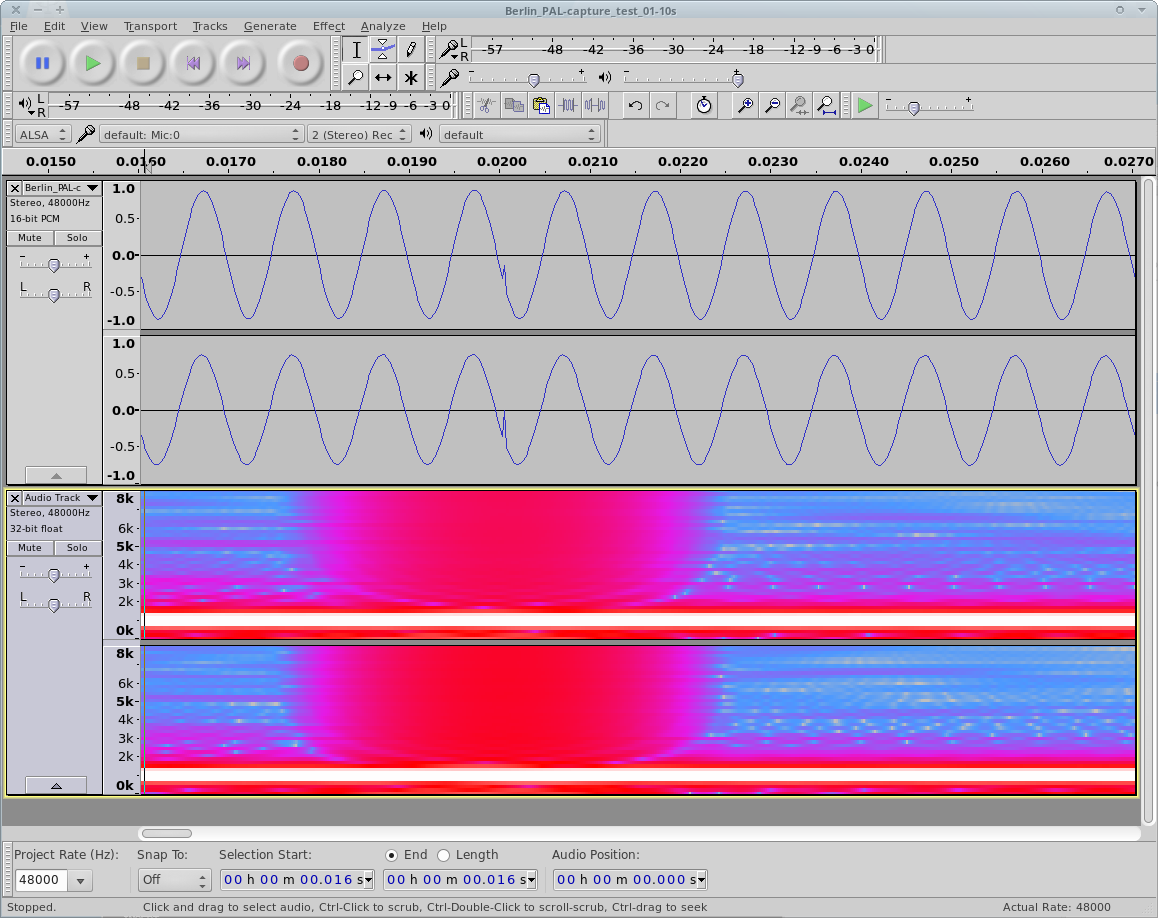
Small Bit, Big Problem
JPEG header “signature” = FF D8 FF DB
- 0xFF = 0b11111111
- 0xBF = 0b10111111
Corruption / Bit rot
“Bit rot can be caused by a number of sources but the result is always the same – one or more bits in the file have changed, causing silent data corruption. The ‘silent’ part of the data corruption means that you don’t know it happened – all you know is that the data has changed (in essence it is now corrupt).” — Jeffrey B. Layton, Linux Magazine, June 2011
Data scrubbing, Fixity checking
How do you know your data is intact?
A check a day keeps the bitrot away…
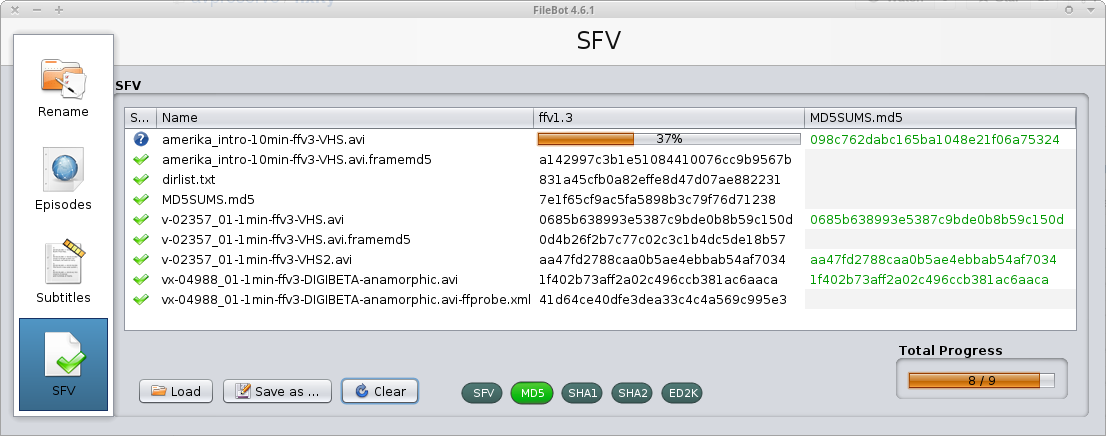
Headcount
Hashcode manifest files can also be used to check if all files expected are present or additional ones exist that are unaccounted for.
Storage: Challenges / Risks
- Storage media failure
- Obsolescence
- Humans
- Catastrophes / War
RAID
Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks
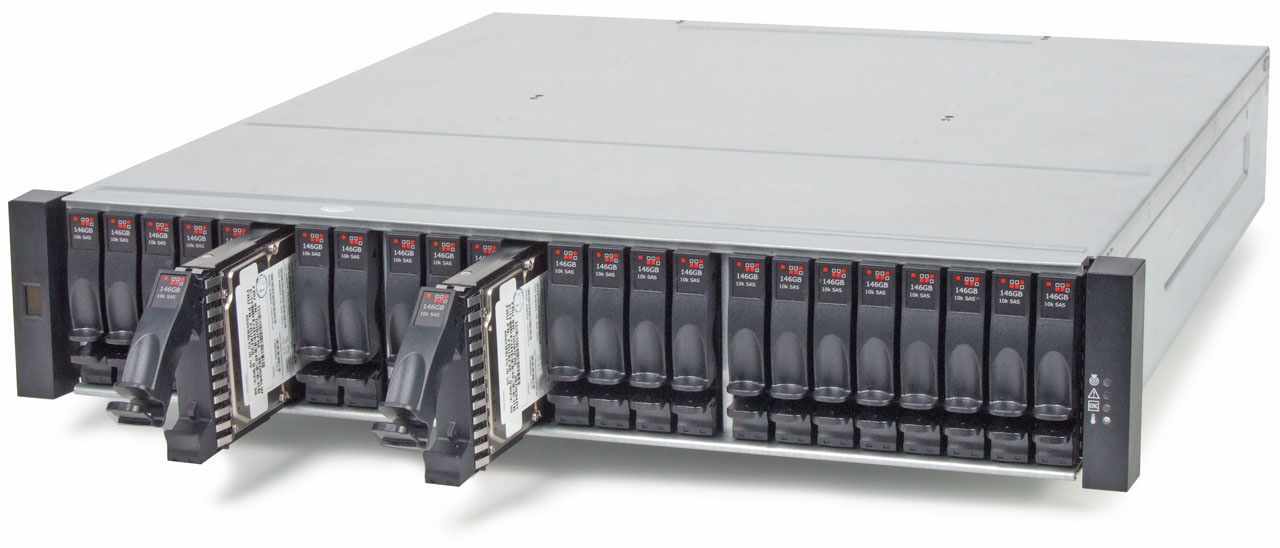

“[…] is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both.”
Source: Wikipedia: RAID
RAID
- Different RAID
levels:
- Stripe = Fast, but dangerous!
- Mirror = Perfect for OS system disks
- RAID5/6 = 1 or 2 disks fault tolerance (parity bits)
- RAID is not a backup.
Sad, but true:
- With > 4TB disks, RAID-6 may be insufficient…
- Long rebuild times may “burn out” the left-over disks.
- ZFS supports 3 disks parity, but … future?
Cluster & replication
- Multiple copies on multiple servers
(“cluster nodes”) - Synchronized (replicated) automatically
- Off-site replication possible
- Replication is not a backup!
- What if a node goes down?
- How does “the cloud” do it?
Inside = The same stuff
- Combining a mix of most (if not all) the above mentioned technologies.
- Mostly unix-like operating systems (e.g. Linux).
- And lots of carriers.
- maintaining it = other people’s problems.
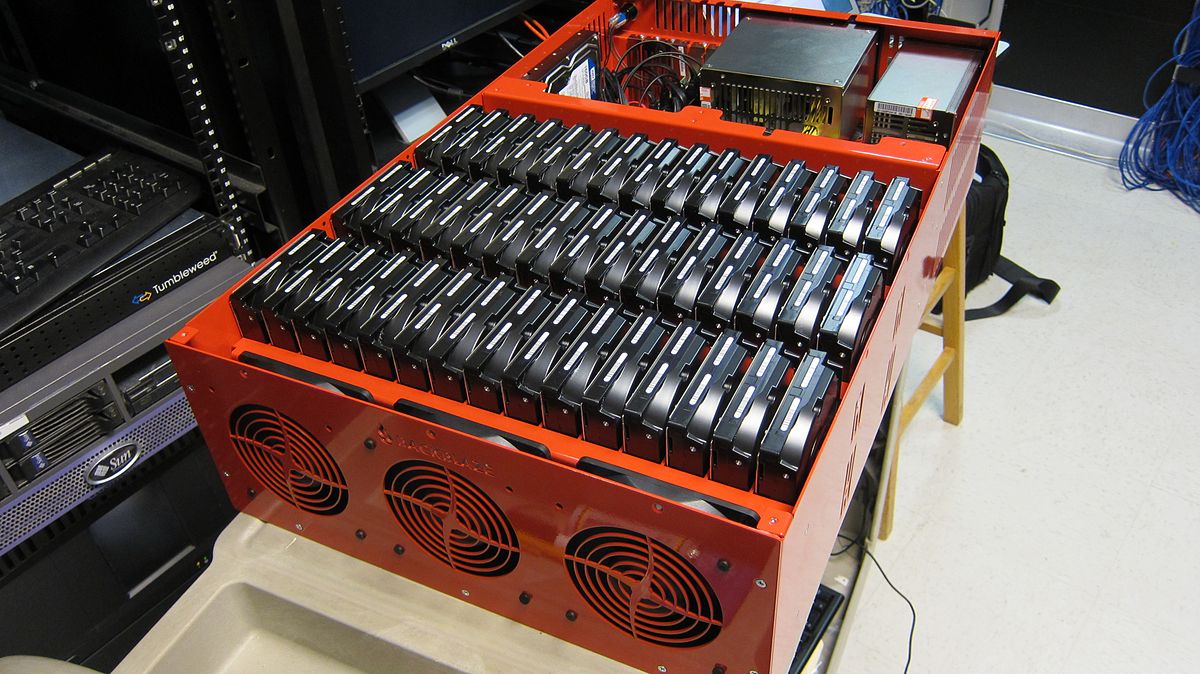

So what if cluster nodes fail?
- Another node takes over.
- Seamlessly. Transparently.
- The faulty node is removed & replaced.
- Life continues.
Erasure Coding
“protects data from multiple drives failure, unlike RAID or replication. For example, RAID6 can protect against two drive failure whereas in MinIO erasure code you can lose as many as half of drives and still the data remains safe.”
Source: MinIO Erasure Code Quickstart Guide
“Compared to data replication, erasure-coding approaches have better performance at reducing storage redundancy and data recovery bandwidth.”
Source: Reliability Assurance of Big Data in the Cloud (2015)
Erasure Coding
- More parity possible than RAID
- Data can be spread across network cluster nodes.
- Does not suffer from rebuild “burn out”.
- More complex to set up & compute.
- Not that widely known/supported/used yet.
Object storage
- Files become “objects”.
- There are no folders (as we’re used to)
- There’s just an identifier.
- Arbitrary metadata may be assigned to each “object”.
- Scales infinitely (theoretically).
- Clusters of block storages with a clever abstraction layer.
Object storage
Beyond classical, hierarchical filesystems
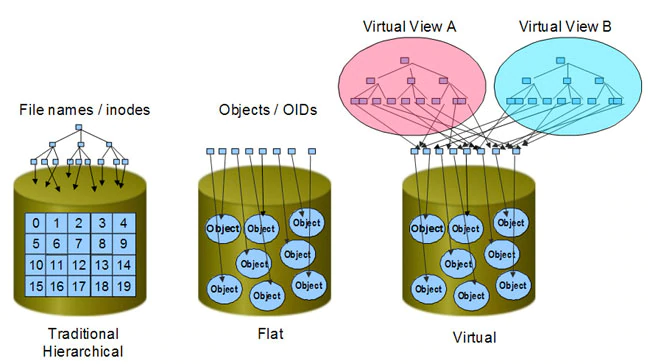
Object storage = The future?
|
Object based storage may very likely replace hierarchical filesystems, but things need to be rewritten/adapted to properly support it. It’s not yet plug-compatible with existing programs. |

|
Object Storage = MAM?
- The object filesystem is an actual catalogue
- If implemented well, the storage itself may be a future DAM/MAM.
- Links/relationships between objects = 🤯🤠🥳
- Combined with LoD, MD Standards & APIs = Wikidata for your files.
- No more distance between file and its catalogue entry.
Just an idea so far, but maybe…?
Software Defined Storage (SDS)
Again: Onions, eh Layers.
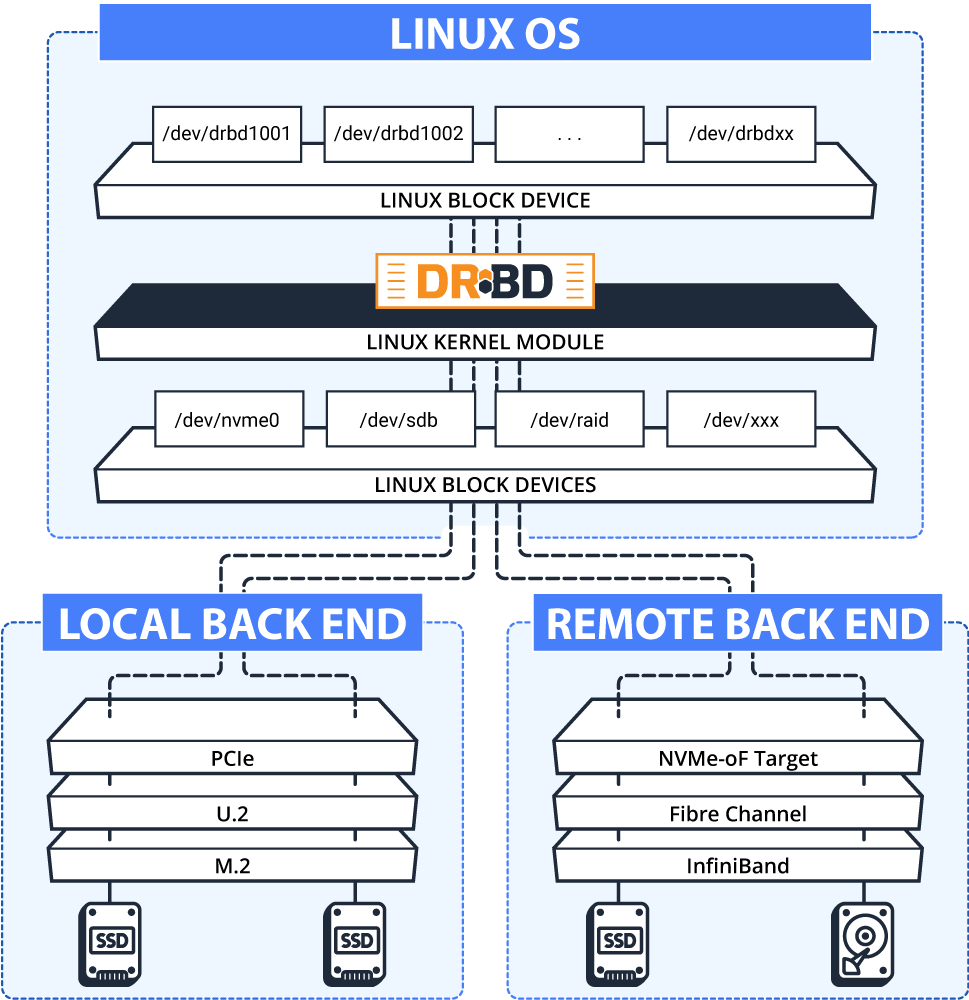
The Cloud
- No internet = no service.
- Make sure your online bandwidth is sufficient.
- Have an exit plan (+contract?) for migration.
- What if their conditions change?
- Where is your data actually stored?
- Does it matter for you? (e.g. legally)
- Again: Consider mixing.
Does it scale?

Does it scale?
- What if you run out of diskspace?
- Need to copy/move everything?
- Or can you simply add “more space”?
- How to know if everything is still “there” and intact?
More Storage Terms
- S.M.A.R.T. Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology
- NAS Network Attached Storage
- SAN Storage Area Network
- RAID Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks
- Object Storage
Good practice
At least 1 backup (=2 copies)
Preferrably 2 backups (=3 copies)
Geographic separate locations (with different threat profile)
Mix storage media
Migrate timely and with a plan (~5-7 years)
Use the right tech for your needs
Periodically check fixity of content and backup
Work with IT to implement and maintain technology.
Comments?
Questions?