Checking AV Properties - Basics
Peter Bubestinger-Steindl
(p.bubestinger @ AV-RD.com)
(p.bubestinger @ AV-RD.com)
April 2022
Abstract
This is about technical properties of audiovisual files, how to identify and check/validate them.
The “Digital Video Trinity”
Structure

Tools
We’ll show these here:
- VLC
- MediaInfo
VLC
- Great videoplayer
- 99% chance you have it on the computer
- Allows quick-check of tech-MD
(Ctrl + J) - For all formats it can play!
Website: videolan.org/vlc
VLC
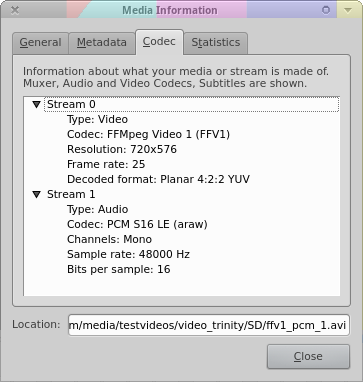
Very handy, but not the best for this job.
MediaInfo
“MediaInfo is a convenient unified display of the most relevant technical and tag data for video and audio files.”
Website: mediaarea.net/MediaInfo
MediaInfo
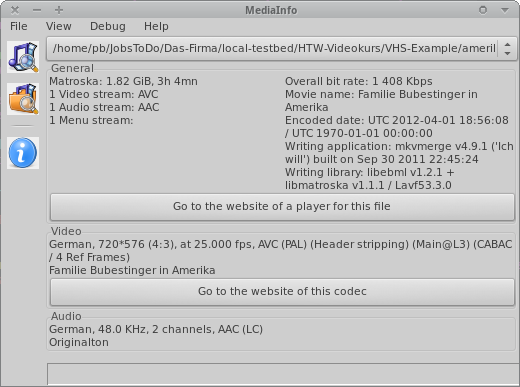
MediaInfo GUI
View ‘Easy’
- General = container level
- Video / Audio
- Other
A/B comparison
(Only in view ‘Easy’)
- Load more than 1 file:
- Select multiple files
- or drag/drop a whole folder
- Scroll dropdown = switch between files
Excellent for a quick spotting of common/different values in a given set.
View ‘HTML’
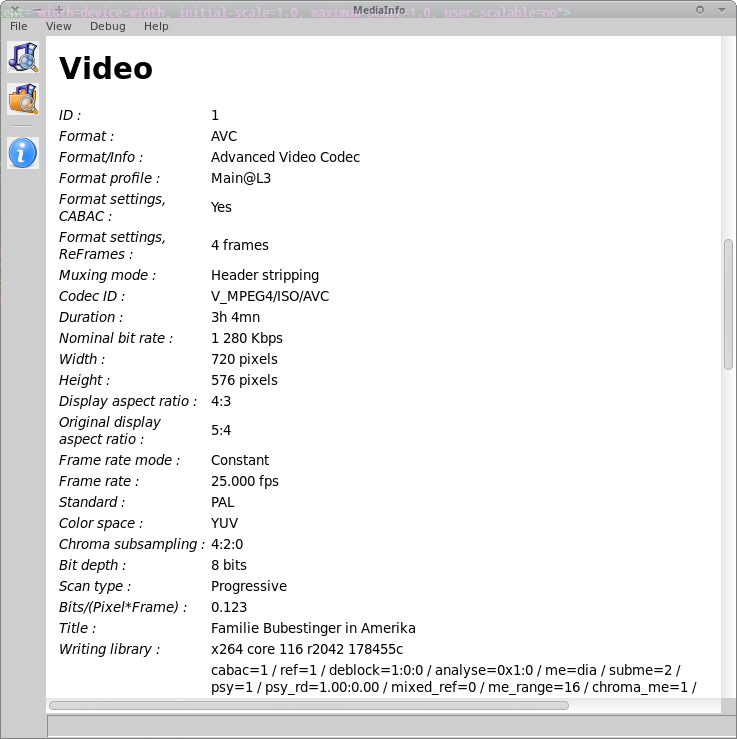
View ‘HTML’
- Nicer to read than view ‘Text’.
- Identical content.
Machine Readable
(aka “parsable output formats”)
- More suited for automated workflows.
- Can be saved from GUI.
- But: Usually commandline.
Machine Readable Output Formats
- XML
- JSON
- CSV
- EBUCore
- PBCore
- MPEG-7
- FIMS
- …
Report to File
Default:
mediainfo myvideo.mkv > myvideo.mkv.mediainfoXML Format (better):
mediainfo --output=XML myvideo.mkv > myvideo.mkv.xml
Parsing Output
Built-in:
mediainfo --Inform="Audio;%Format%" myvideo.mkv
Using “xmlstarlet”:
xmlstarlet sel -t -m \
"//_:media/_:track[@type='Audio']" \
-c . -n \
myvideo.xml`
Comments?
Questions?