Codecs - Basics
(p.bubestinger@av-rd.com)2021-09
Hello again! :)
Codecs - Basics
What would you like to know?
Why bother?
Just use the format that is:
- Best quality
- Smallest size
- Fastest speed
- Super robust
- Seamlessly interoperable
- Most convenient
- Preservable like a rock
Which media formats do you know?
The “Digital Video Trinity”
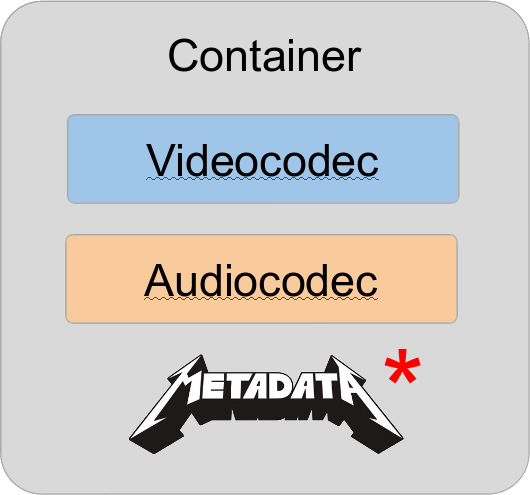
Triplet notation
Helps reducing confusions:
- H.264 / AAC in MP4
- FFV1 / PCM in MKV
- IMX / PCM in MXF
- etc
Codec? Container?
What’s a Codec?
Think of a human language…
- It’s coded information.
- There may be dialects.
- Different implementations may
“speak / understand” differently.
What’s a Container?
Think of a regular paper folder…
- It’s a wrapper around content.
- Contains Metadata.
- Structures the content streams.
Data Streams
- What is a “stream”?
- Types: audio, video, timecode, subtitle, etc.
- A+V sync: correct timestamps?
Let’s look inside! :)
VLC
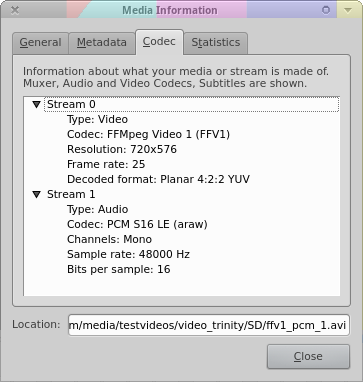
Very handy, but not the best for this job.
Website: videolan.org/vlc
MediaInfo
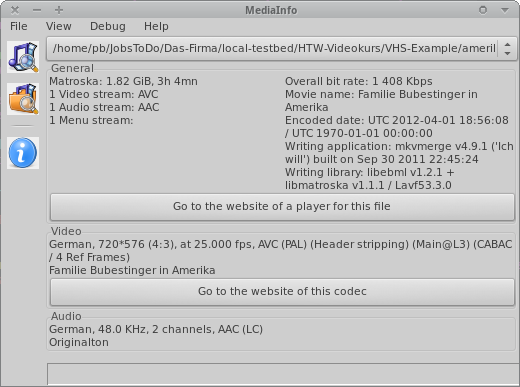
“MediaInfo is a convenient unified display of the most relevant technical and tag data for video and audio files.” (mediaarea.net/MediaInfo)
Format choice
Considerations
Your use cases
“Different strokes for different folks”
- Production, Preservation, Access
- Who will want/need to work with these files?
- Under which conditions?
- For how long?
- Which properties are significant to you?
Significant properties
Knowing and deciding which properties to safeguard and which are allowed to change.
See:
Nestor: Leitfaden DLTP AV Medien
LoC FADGI: DRAFT Significant Properties for Digital Video
Quality
- Avoid generation loss (if possible).
- Avoid rescaling.
- Don’t invent more bits.
- Preserve “pix_fmt”.
- More headroom for lower quality?
- Use high enough bitrate.
Size
- What is the “bitrate” for?
- lossy vs lossless vs uncompressed?
- What is “Constant Rate Factor (CRF)” for?
- Uncompressed != Uncompressed?
(Ex: RGB, BGR, UYVY, YUY2, V210, etc)
Performance
Often a tradeoff between:
- Processing power (CPU/RAM)
(format/algorithm complexity) - I/O bandwidth (disk/network)
(data size)
Preservation Format
- Can be used to generate all other versions.
- No artifical restrictions for using it.
Now and under unknown future conditions. - Well documented, no secrets, FOSS implementation exists.
- Bit error resilience would be nice.
- As simple as possible, as complicated as necessary
Summarized as: “preserves well.”
Preservation Format
Decisions. Again.
- May be “less practical” for editing/access.
- What about FFV1/PCM/MKV?
- Image sequence vs videofile?
Open vs Closed

Open vs Closed
Representation Information (OAIS):
[…] maps the physical bit level information into the content concepts addressed by the creator of the digital object, an example is the ASCII format which describes how the bits are represented."
Popular combinations
| Video | Audio | Container | Domain |
|---|---|---|---|
| XDCAM | PCM | MXF | Broadcast |
| H.264 | AAC | MP4 | Consumer |
| FFV1 | PCM, FLAC | MKV, MOV, AVI | Preservation |
| v210 | PCM | MOV, MXF | Preservation |
| ProRes | PCM | MOV | Production |
| MPEG-2 | AC3 | MPG | DVD |
| DV | PCM | AVI/DV | DV |
| MPEG-2 | MP2 | M2T(=MPG) | HDV |
| XviD | MP3 | AVI | Retro |
| DPX, TIFF | WAV(=PCM) | Folder | Film |
Audio
- Preservation format: PCM in WAV
- WAV = PCM = RIFF = AVI?
Format normalization
- What is this?
- When to do it?
- Practical: Whitelist approach
- Helper: MediaConch
- FIN -
Questions & Comments welcome! :)
Peter Bubestinger-Steindl
p.bubestinger@av-rd.com