Topic 1 - Digital Files
Peter Bubestinger
2021-05-04
File Format Considerations
The Goal

* Best quality * Preserve original properties * Last forever * Lowest size * Fast and easy to open/use * +cherries & ice cream on top * ...
Data Structure
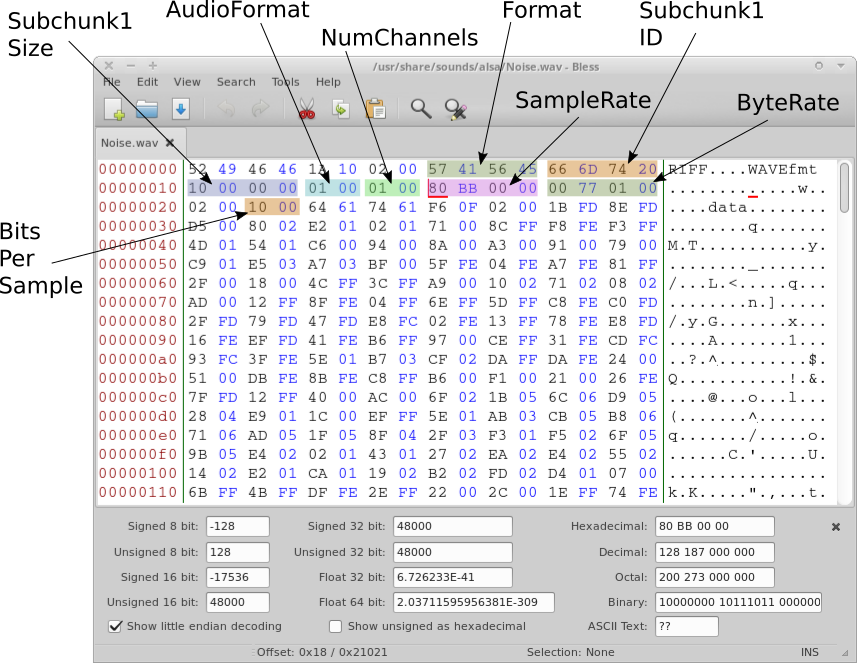
Digital Video Trinity
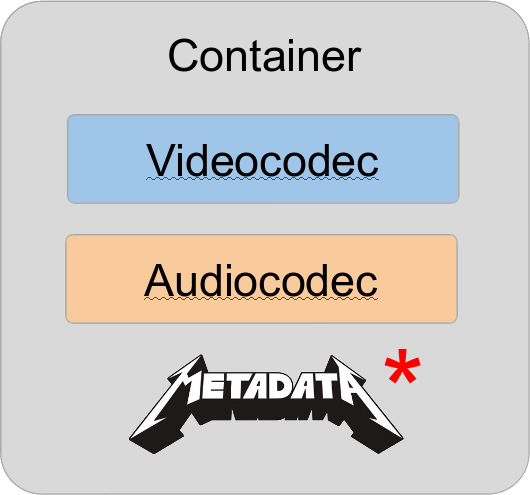
Remember?
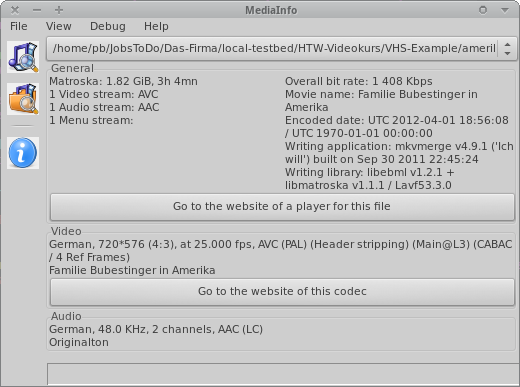
Characteristics
Image
| File 1 | File 2 | File 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Format | TIFF 6.0 | TIFF 6.0 | TIFF 4.0 |
| Colorspace | RGB | CMYK | Grayscale |
| DPI | 600 dpi | 150 dpi | 150 dpi |
| Resolution | 4328 x 2979px | 1024 x 768 | 1024 x 768 |
Characteristics
Audiovisual
| File 1 | File 2 | File 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Format | MOV | MOV | MOV |
| Resolution | 720 x 576px | 1920 x 1080 | 640 x 480 |
| FPS | 25 | 24 | 29.97 |
| Samplerate | 48 kHz | 48 kHz | 44.1 kHz |
| Channels | Stereo | Surround 5.1 | Mono |
Data rate / Filesize
| Type | Duration | Bitrate | Filesize |
|---|---|---|---|
| Video | 1 hour | 210 Mb/s | 92 GB |
| 50 Mb/s | 22 GB | ||
| 25 Mb/s | 11 GB | ||
| 1,5 Mb/s | 1 GB | ||
| Audio | 1 hour | 4,6 Mb/s | 2 GB |
| 128 kb/s | 56 MB |
Different Formats, different use cases
- Preservation
- Mezzanine
- Access
Different Formats, different use cases
Preservation: Stand the test of time.
Highest original quality.Mezzanine: For daily work.
High quality.Access For quick and easy access.
Quality not necessarily best/high.
Examples: Video
- Preservation:
* Uncompressed * FFV1 * J2K-lossless * ...
- Mezzanine:
* ProRes * H.264 * DVCPRO50 * ...
- Access:
* MP4 * WebM * DVD * BluRay * ...
Size (still) matters
| Type | Duration | Bitrate | Filesize | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Video | 1 hour | 210 Mb/s | 92 GB | Preservation |
| 50 Mb/s | 22 GB | Preservation | ||
| 25 Mb/s | 11 GB | Preservation / Mezzanine | ||
| 1,5 Mb/s | 1 GB | Access | ||
| Audio | 1 hour | 4,6 Mb/s | 2 GB | Preservation |
| 128 kb/s | 56 MB | Access |
Data rate = Bitrate
- Mbps / 8 = MB / second
- MB/s * 60 = MB / minute
- MB/min * 60 = MB / hour
Significant properties
- Depends on media type.
- Examples for A/V:
- resolution
- framerate
- aspect ratio
- colorspace
- subsampling
- ...
More: FADGI Significant Properties for Digital Video - DRAFT
Significant properties
Image?
Significant properties
Audio?
Lossy, Lossless, Uncompressed?
How it affects quality and preservation.
Lossy

Generation Loss

Lossless
"It's like ZIP for film!"
- No generation loss
- Way larger than lossy
- Smaller than uncompressed
Uncompressed
- No generation loss
- Dead simple (=preserves well)
- The largest possible version
- There's more than just 1 "uncompressed"
Uncompressed - Think of it as:
1px RGB Image:
RRR GGG BBB AAA1px YUV Image:
YYY UUU VVV1 sample audio:
LLLLLLLL RRRRRRRRUncompressed Image
- Width(px) x Height(px)
- x Bits-Per-Pixel(bpp)
- x FPS
- / 8 = 1 second (in Byte)
Uncompressed Audio
- Samplerate x bit-depth
- x channels (even if silence!)
- / 8 = 1 second (in Byte)
Default Formats
Film:
- Image: DPX / TIFF files
- Audio: PCM in WAV
- Metadata: Mostly sidecar, some MD in image files.
Video:
- Image: Default = lossy encoding
- Audio: production = PCM, consumer = AAC
- Metadata: Often embedded. Sometimes sidecar.
Best practices for A/V Formats
Capture analog video uncompressed (v210) or lossless (FFV1, J2K) to avoid adding digital generation loss.
Or as fallback option:
At the highest quality (data rate) you can store and manage well over time.Capture digital tape in its native format without generation loss (MiniDV, DAT, DigiBeta, etc.)
Store born-digital files "as original" as possible.
Audio preservation format is uncompressed WAV (PCM) for analog originals.
For video container formats, consider using MKV or MOV.
MXF only for broadcast.Choose formats that can be kept alive (=open & documented)
File formats and preservation implications
Complexity

Format Support
- Popular?
- Documented?
- Well supported?
- Can you handle/access it beyond shelf-life?
Obsolescence: Open vs Closed
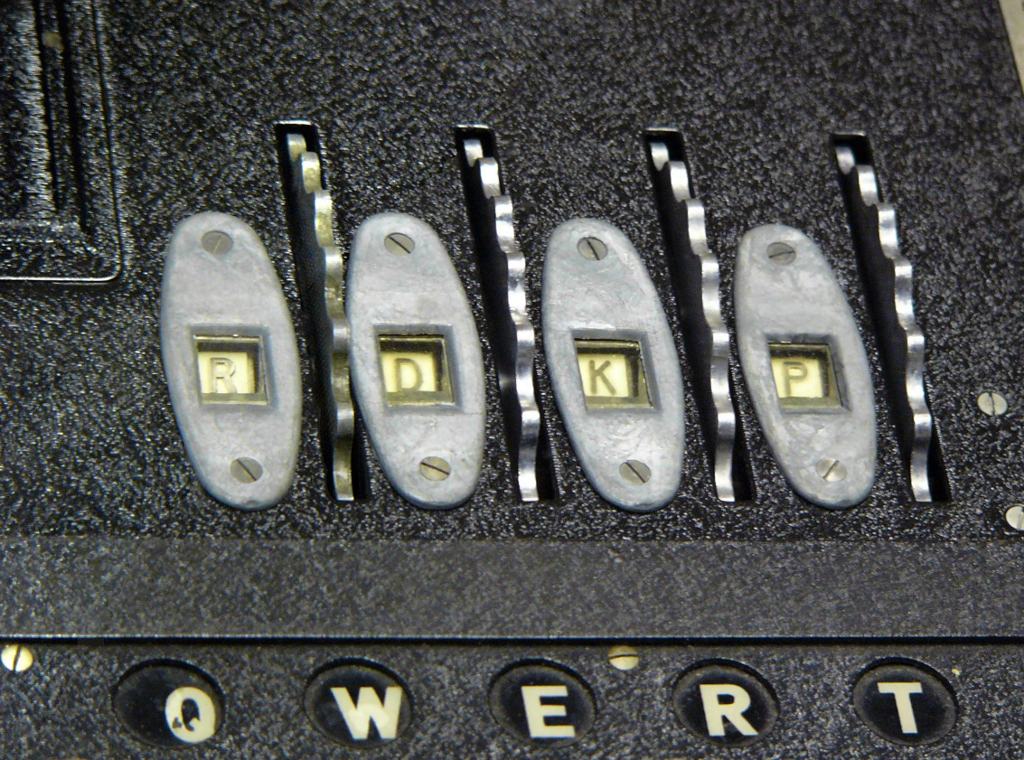

Theory vs Practice


Schematics
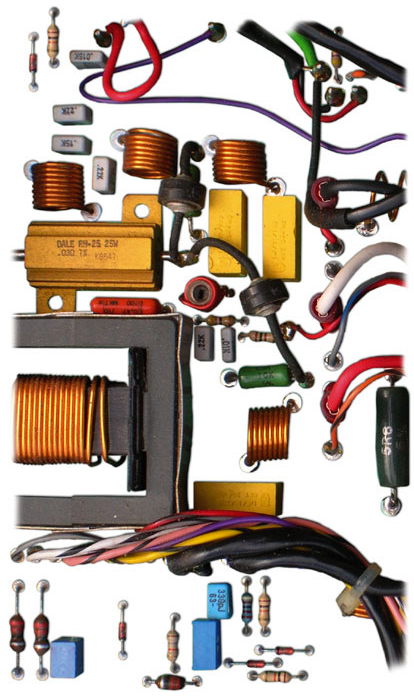
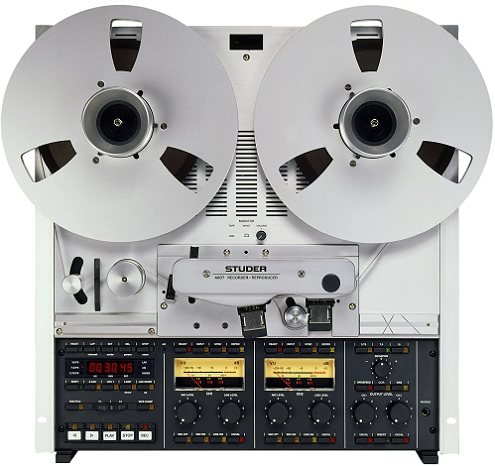


Error resilience

Popular formats
Containers
- AVI: Audio Video Interleave
- MOV: Quicktime
- MKV: Matroska Video
- MXF: Material eXchange Format
- WAV / RIFF
- MPG, MTS: MPEG Transport Stream
Video Codecs
Audio
- AAC
- MP3
- Opus
- PCM
- FLAC
Risks to format longevity
- Data errors
- Obsolescence
- Interoperability issues
- Vendor lock-in
Countermeasures?
Comments?
Questions?