Data Integrity
Peter Bubestinger-Steindl
(p.bubestinger@av-rd.com)
November 2019
Data Integrity
What is that?
What is “Fixity”?
Hashcodes
raw.txt
“This is a raw text file.”
MD5 = b3a243d2443037a783c8799fe2c4926a
Hashcodes
raw.txt
“This is a raw text file.⎕”
MD5 = 7096384353da7d8cb59b1395e63d1250
Hashcodes
raw.txt
“this is a raw text file.”
MD5 = a94a15d1b72bbfee7997bf237cf0347e
Hashcodes
raw-text.txt
“this is a raw text file.”
MD5 = a94a15d1b72bbfee7997bf237cf0347e
Different algorithms
- CRC
- MD5
- SHA .. 1 .. 2 .. 256 .. SHA512?
- WTF
Hashcode Examples
- CRC =
4294967295
- MD5 =
d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
- SHA256 =
e3b0c44298fc1c149afbf4c8996fb92427ae41e4649b934ca495991b7852b855
Fixity creation
Generate hashes as early as possible in a file’s lifecycle.
Different levels
- Filesystem
- File (=data)
- Content (=payload)
Level 1
$ ls -la --time-style=full-iso
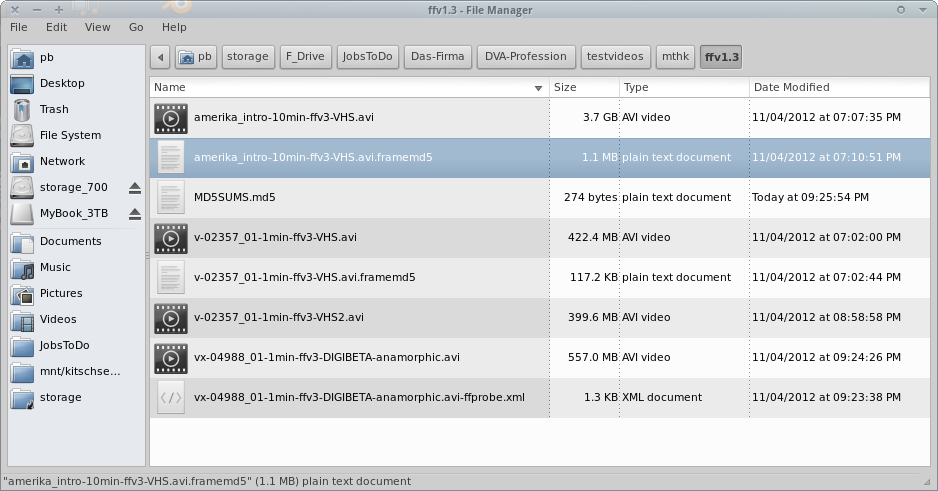 Filesystem
Filesystem
Level 2
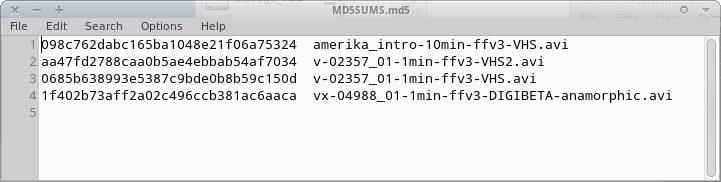 Plain text manifest file
Plain text manifest file
Level 3
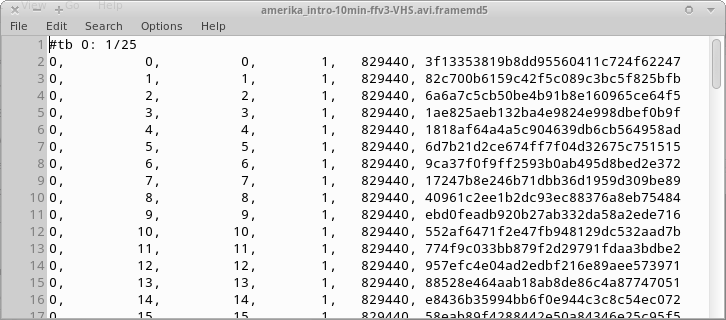 Content payload “framemd5”
Content payload “framemd5”
HashCheck
GUI to handle hashcodes (Windows only).
Website: code.kliu.org/hashcheck
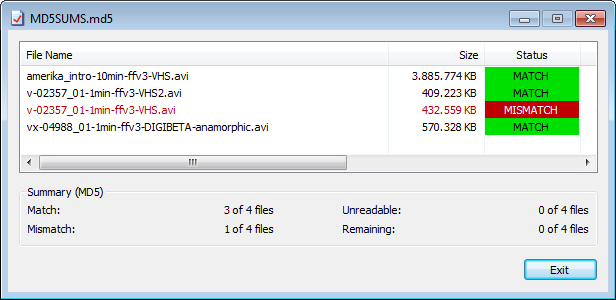 HashCheck showing a mismatch error
HashCheck showing a mismatch error
LoC BagIt “Bags”
“Bags have built-in inventory checking, to help ensure that content transferred intact.”
Bagger
A GUI for handling BagIt bags.
Bagger
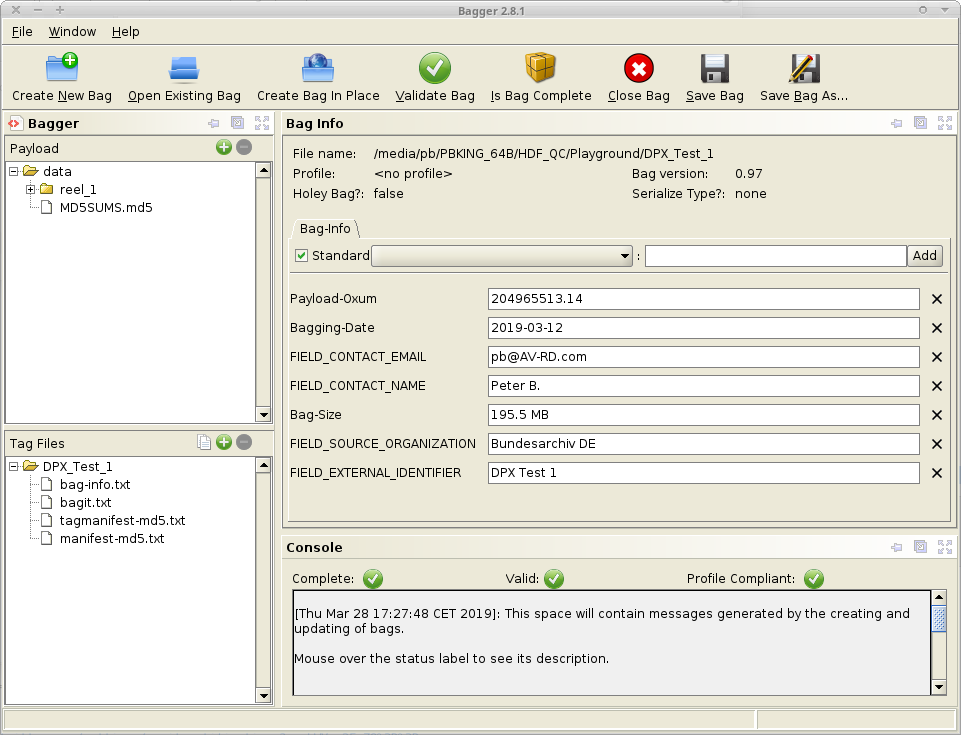 Bagger GUI
Bagger GUI
Hashcode use: When?
- Ingest into preservation environment
- Periodically in storage/backup
- During transfers or access
- Deduplification
Data Integrity Playtime!







Comments?
Questions?